If You Want I Could Giveyou a Television and Eyes of Blue
The strange power of the 'evil eye'
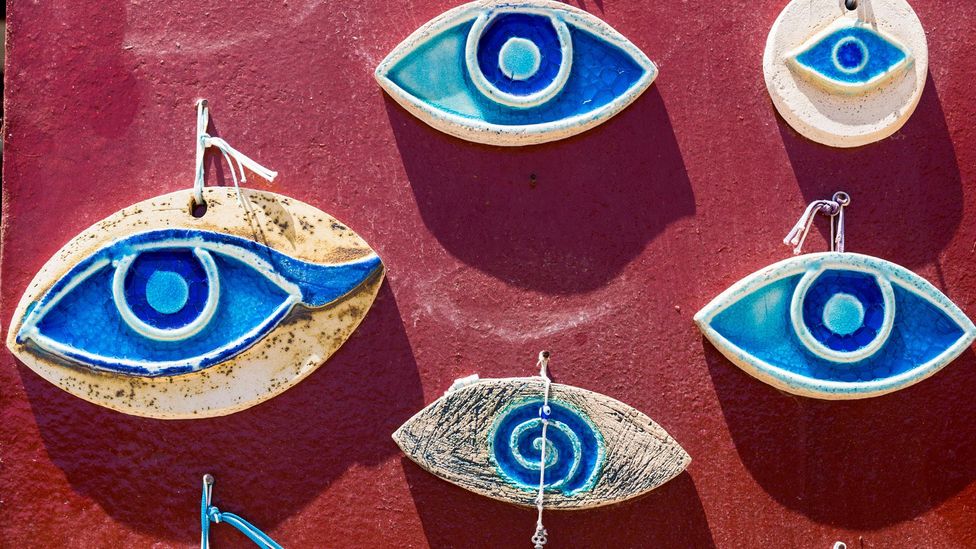

From the Eye of Horus to Gigi Hadid, 'for thousands of years the eye has maintained its steady hold on the human imagination,' writes Quinn Hargitai.
W
When it comes to warding off the mystic malevolent forces of the world, there is perhaps no charm more recognised or renowned than the 'evil eye'. Ubiquitous in its use, the striking image of the cobalt-blue eye has appeared not only in the bazaars of Istanbul, but everywhere from the sides of planes to the pages of comic books.
In the last decade, evil eye imagery has most frequently appeared in the world of fashion. Kim Kardashian has been photographed on numerous occasions sporting bracelets and headpieces featuring the symbol, while fashion model Gigi Hadid jumped on the trend in late 2017, announcing that she would be launching the EyeLove shoe line.
- How Paris changed how we think
- The language gay men used to survive
- The insect that painted Europe red
This recent endorsement from A-list celebrities has resulted in the surfacing of countless online tutorials for making your own evil eye bracelets, necklaces and keychains. Though all this attention would suggest the evil eye is seeing a sudden surge in popularity, the truth is that for thousands of years the symbol has maintained its steady hold on the human imagination.

Eye idols carved out of gypsum alabaster have been excavated at Tell Brak, Syria and are believed to date from before 3500 BC (Credit: Metropolitan Museum of Art)
To understand the origins of the evil eye, one must first understand the distinction between the amulet and the evil eye itself. Though often dubbed as 'the evil eye', the ocular amulet is actually the charm meant to ward off the true evil eye: a curse transmitted through a malicious glare, usually one inspired by envy. Though the amulet – often referred to as a nazar – has existed in various permutations for thousands of years, the curse which it repels is far older and more difficult to trace.
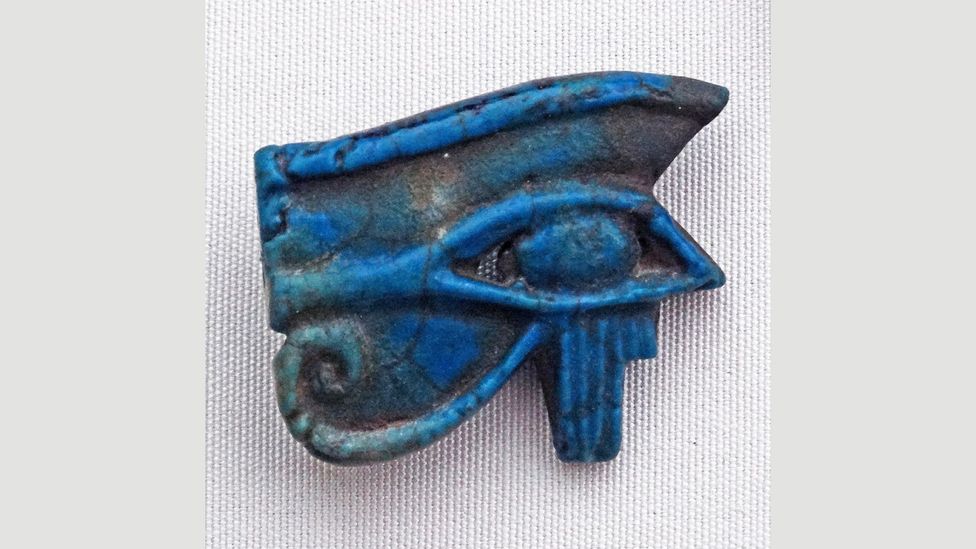

In ancient Egypt, the Eye of Horus, also known as a Wadjet pendant, was buried with pharaohs to protect them in the afterlife (Credit: Alamy)
In essence, the curse of the evil eye is not a complicated concept; it stems from the belief that someone who achieves great success or recognition also attracts the envy of those around them. That envy in turn manifests itself as a curse that will undo their good fortune. The concept is well captured by Heliodorus of Emesa in the ancient Greek romance Aethiopica, in which he writes, "When any one looks at what is excellent with an envious eye he fills the surrounding atmosphere with a pernicious quality, and transmits his own envenomed exhalations into whatever is nearest to him."
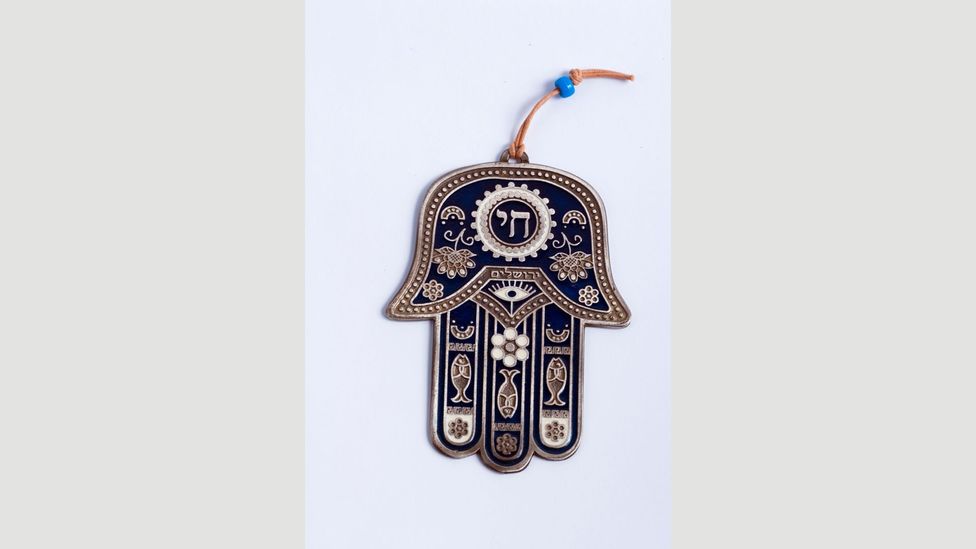

The Hamsa is an amulet in the shape of a palm with an eye in the middle embraced by Jews, Christians and Muslims in North Africa and the Middle East (Credit: Alamy)
The belief in this curse spans cultures as well as generations; to date one of the most exhaustive compilations of legends regarding the evil eye is Frederick Thomas Elworthy's The Evil Eye: The Classic Account of an Ancient Superstition. Elworthy explores instances of the symbol in a number of cultures; from the petrifying gaze of Greek gorgons to Irish folktales of men able to bewitch horses with a single stare, virtually every culture has a legend related to the evil eye. The eye symbol is so deeply embedded in culture that, in spite of its potentially pagan connotations, it even finds a place within religious texts, including the Bible and the Quran.
An eye for an eye
Belief in the evil eye has transcended mere superstition, with a number of celebrated thinkers attesting to its veracity. One of the most notable examples was the Greek philosopher Plutarch, who in his Symposiacs suggested a scientific explanation: that the human eye had the power of releasing invisible rays of energy that were in some cases potent enough to kill children or small animals. What's more, Plutarch claims that certain people possessed an even stronger ability to fascinate, citing groups of people to the south of the Black Sea as being uncannily proficient at bestowing the curse. More often than not, those said to be most adept at delivering the curse are blue-eyed, likely due to the fact that this is a genetic rarity in the Mediterranean area.
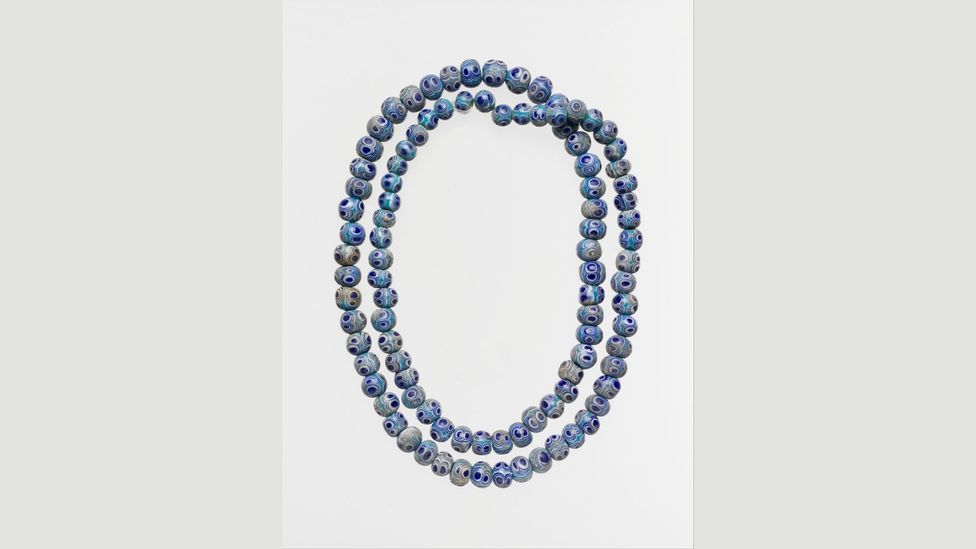

The ancient Phoenicians put eye symbols on beads they strung together as necklaces (Credit: Metropolitan Museum of Art)
Though the theory that some possess a more potent glare capable of inflicting harm is quite common in the lore of the evil eye, not all correlate the power with an inherent ill will. Some cultures view the ability to bestow the curse as an unfortunate burden, a curse in itself. For instance, Elworthy makes reference to an archaic Polish folk tale that tells of a man whose gaze was such a potent carrier of the curse that he resorted to cutting out his own eyes rather than continuing to spread misfortune to his loved ones.
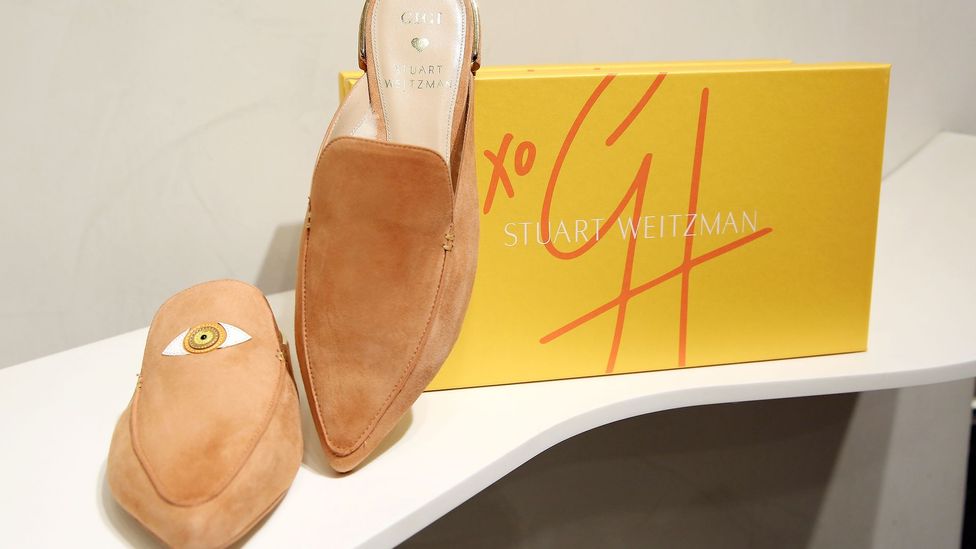

Gigi Hadid, whose father is Jordanian-American of Palestinian descent, has a line of shoes featuring the eye symbol called EyeLove (Credit: Getty Images)
With such an ardent and widespread belief that a stare held the power to inflict catastrophic misfortune, it's no surprise that the people of these ancient civilizations sought out a means to repel it, which led to the earliest iterations of the nazar amulet that we know today. Just how far back do these go? "The earliest version of eye amulets goes back to 3,300 BC," Dr Nese Yildiran, an art history professor at Istanbul's Bahçeşehir University, tells BBC Culture. "The amulets had been excavated in Tell Brak, one of the oldest cities of Mesopotamia – modern day Syria. They were in the form of some abstract alabaster idols made with incised eyes."
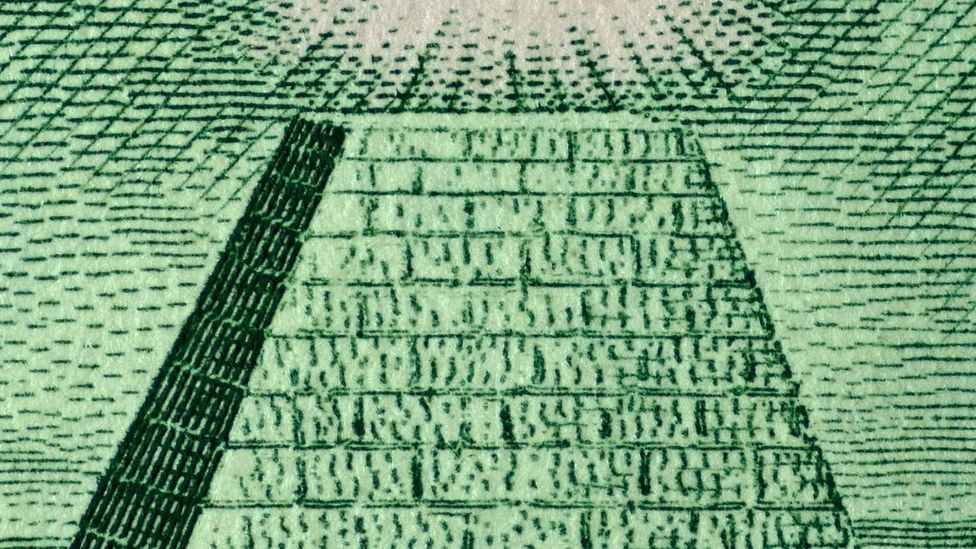

The Eye of Providence, often embraced by Freemasons and meant to symbolise God's omniscience, appears on the back of the US one-dollar bill (Credit: Alamy)
While the alabaster idols of Tell Brak seem to be one of the oldest eye amulets discovered, they are a far cry from the typical blue glass we know today, the earliest iterations of which didn't begin appearing in the Mediterranean until around 1500 BCE. How were these early prototypes of Tell Brak distilled into the more modern versions?
"The glass beads of the Aegean islands and Asia Minor were directly dependent upon improvements in glass production," Yildiran explains. "As for the colour blue, it definitely first comes from Egyptian glazed mud, which contains a high percentage of oxides; the copper and cobalt give the blue colour when baked."
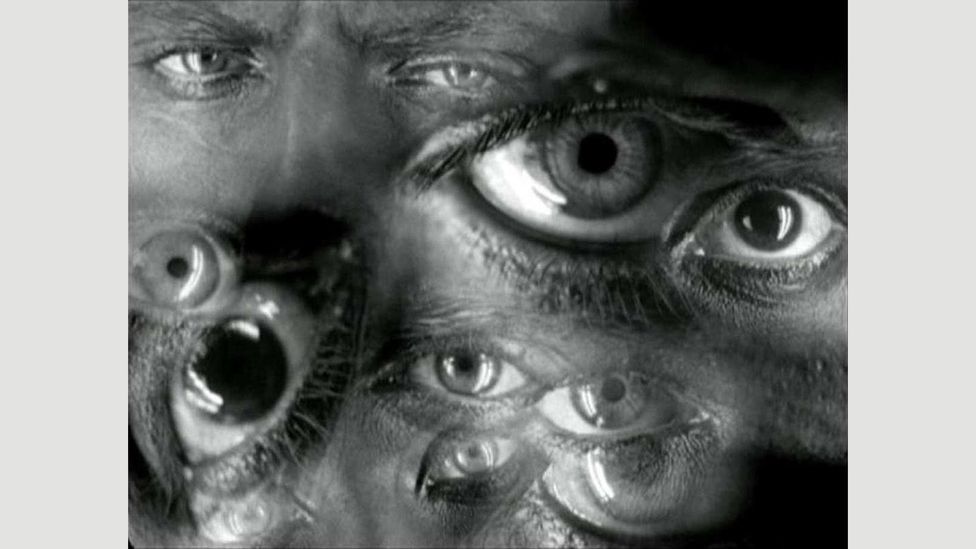

The eye has come to represent surveillance and the fear of being watched, as in Fritz Lang's 1927 silent sci-fi film Metropolis (Credit: Kino)
Yildiran makes reference to several blue Eye of Horus pendants excavated in Egypt, asserting that these could in a way be seen as the most influential predecessor to the modern nazar. According to Yildiran, early Turkic tribes held a strong fascination with this shade of blue because of its connections with their sky deity, Tengri, and likely co-opted the use of cobalt and copper as a result.
The blue evil eye beads underwent a widespread circulation in the region, being used by the Phoenicians, Assyrians, Greeks, Romans and, perhaps most famously, the Ottomans. Though their usage was most concentrated in the Mediterranean and the Levant, through means of trade and the expansion of empires the blue eye beads began to find their way to all different corners of the globe.
Blind to its meaning?
What's most fascinating about the evil eye isn't its mere longevity, but the fact that its usage has deviated little over the course of millennia. We're still affixing the evil eye to the sides of our planes in the same way that the Egyptians and Etruscans painted the eye on the prows of their ships to ensure safe passage. It's still a tradition in Turkey to bring an evil eye token to newborn babies, echoing the belief that young children are often the most susceptible to the curse.
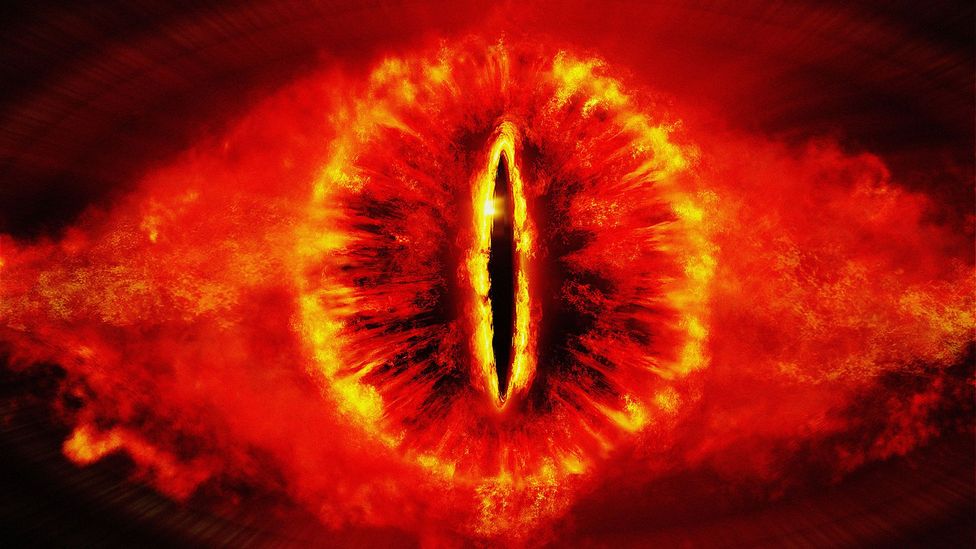
In The Lord of the Rings, the Dark Lord Sauron is a supreme intelligence that exists as a disembodied eye, holding all of Middle Earth under his gaze (Credit: Alamy)
But one can't help but wonder if as the eye morphs along with the mediums of the modern world, its meaning and history will eventually fall by the wayside. Some current interpretations have already incited fears of cultural appropriation, especially regarding fashion's use of the evil eye in the Hamsa, which holds a sacred place in both Judaism and Islam.
The eye's history is far-reaching and intertwines with many peoples, so many of the modern users do in fact hold a connection to it in terms of heritage; the aforementioned Kim Kardashian and Gigi Hadid, for instance, both hail from cultures in which the evil eye is a staple.
Yildiran doesn't believe it is an issue."The evil eye transcends this concern because it has been a part of a rather big geography, and open to all sorts of practices. It's not difficult to imagine we will keep seeing motifs derived from the evil eye."
Although the symbol may have the ability to transcend boundaries – be they cultural, geographical or religious – it may be worth considering its meaning beyond a mere trinket or fashion statement. The evil eye is a remnant from the very dawn of civilisation, harking back to some of humanity's most enduring and profound beliefs. To wear an amulet flippantly without such knowledge might not only render its protective abilities useless, but incur an even more potent curse – if that's something you believe in, of course.
If you would like to comment on this story or anything else you have seen on BBC Culture, head over to our Facebook page or message us onTwitter .
And if you liked this story, sign up for the weekly bbc.com features newsletter , called "If You Only Read 6 Things This Week". A handpicked selection of stories from BBC Future, Culture, Capital and Travel, delivered to your inbox every Friday.
Source: https://www.bbc.com/culture/article/20180216-the-strange-power-of-the-evil-eye
0 Response to "If You Want I Could Giveyou a Television and Eyes of Blue"
Post a Comment